A thorough assessment of the heart provides valuable information about the function of a patient’s cardiovascular system. Understanding how to properly assess the cardiovascular system and identifying both normal and abnormal assessment findings will allow the nurse to provide quality, safe care to the patient.
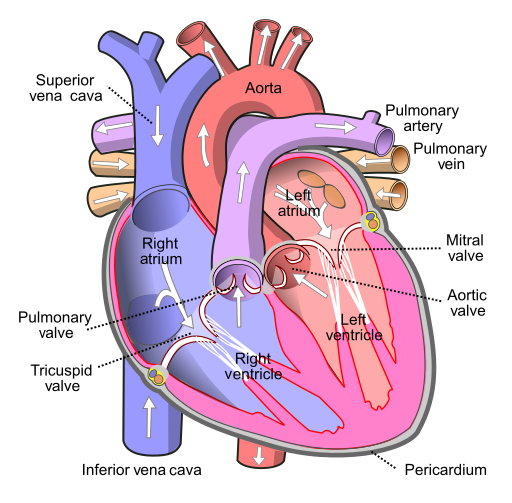
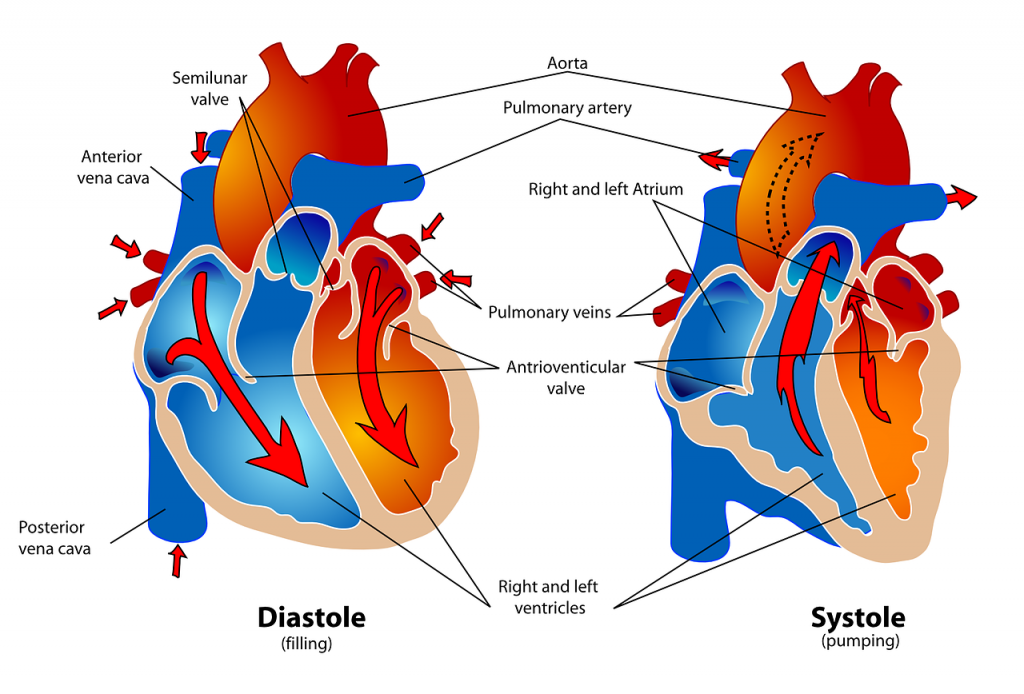
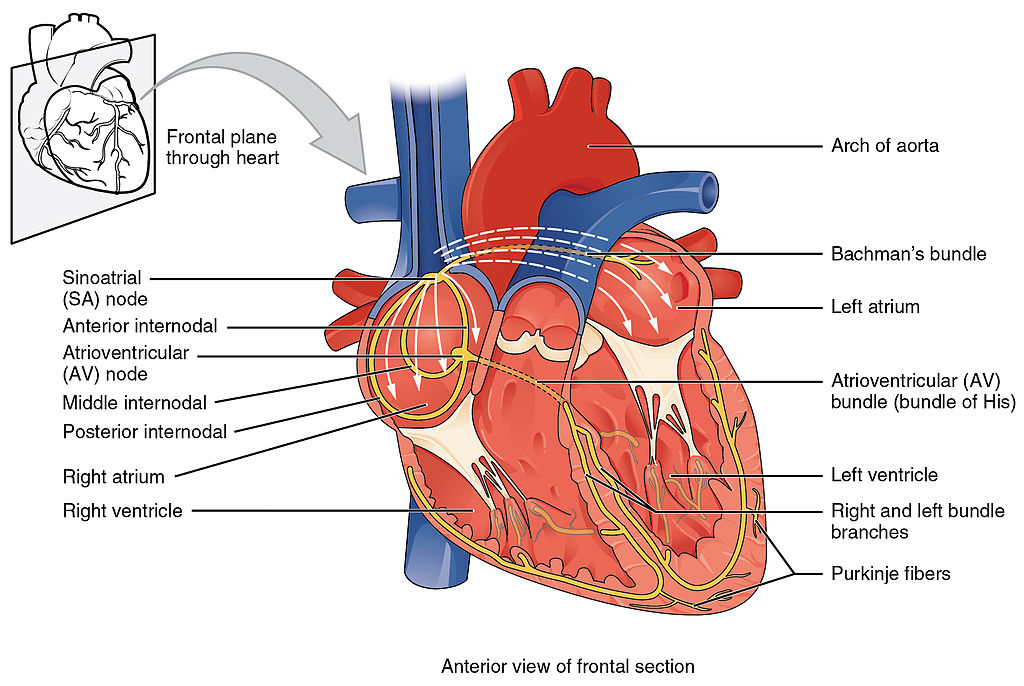
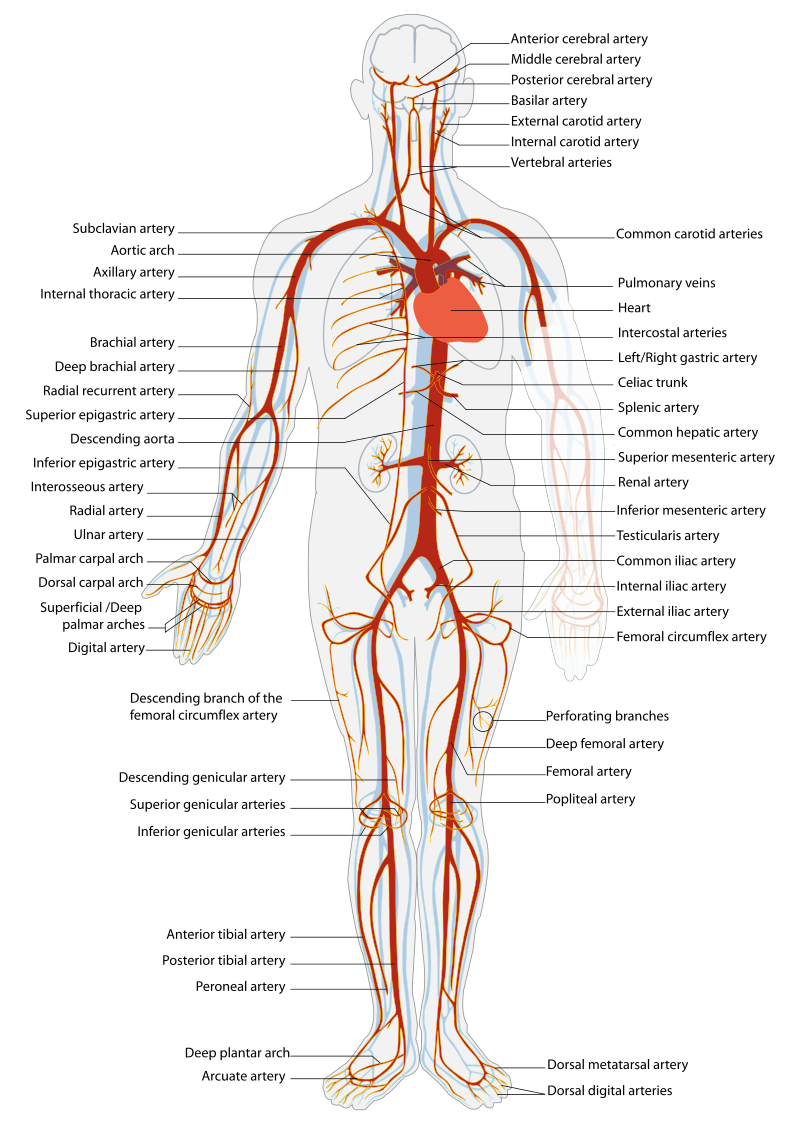
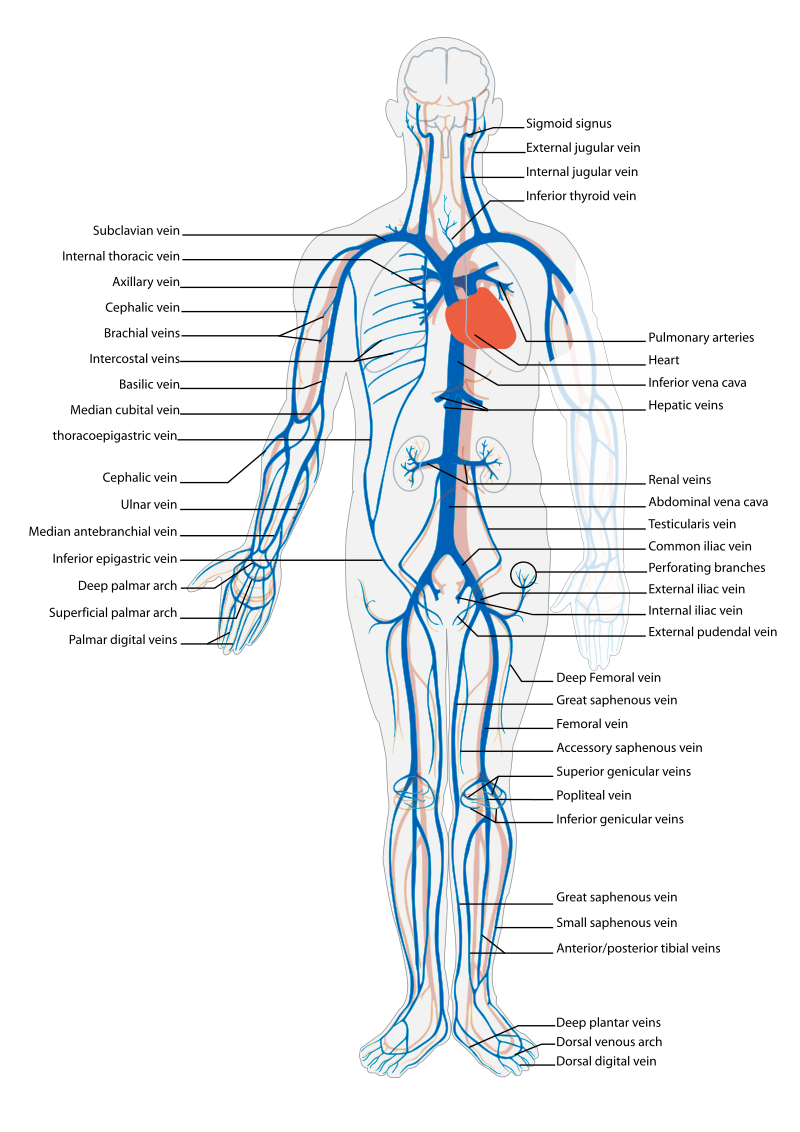
Before assessing a patient’s cardiovascular system, it is important to understand the various functions of the cardiovascular system. In addition to the information provided in the “Review of Cardiac Basics” section, the following images provide an overview of the cardiovascular system. Figure 9.1 [1] provides an overview of the structure of the heart. Note the main cardiac structures are the atria, ventricles, and heart valves. Figure 9.2 [2] demonstrates blood flow through the heart. Notice the flow of deoxygenated blood from the posterior and superior vena cava into the right atria and ventricle during diastole (indicated by blue coloring of these structures). The right ventricle then pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery during systole. At the same time, oxygenated blood from the lungs returns to the left atria and ventricle via the pulmonary veins during diastole (indicated by red coloring of these structures) and then is pumped out to the body via the aorta during systole. Figure 9.3 [3] demonstrates the conduction system of the heart. This image depicts the conduction pathway through the heart as the tissue responds to electrical stimulation. Figure 9.4 [4] illustrates the arteries of the circulatory system, and Figure 9.5 [5] depicts the veins of the circulatory system. The purpose of these figures is to facilitate understanding of the electrical and mechanical function of the heart within the cardiovascular system.





Assessing the cardiovascular system includes performing several subjective and objective assessments. At times, assessment findings are modified according to life span considerations.
The subjective assessment of the cardiovascular and peripheral vascular system is vital for uncovering signs of potential dysfunction. To complete the subjective cardiovascular assessment, the nurse begins with a focused interview. The focused interview explores past medical and family history, medications, cardiac risk factors, and reported symptoms. Symptoms related to the cardiovascular system include chest pain, peripheral edema, unexplained sudden weight gain, shortness of breath (dyspnea), irregular pulse rate or rhythm, dizziness, or poor peripheral circulation. Any new or worsening symptoms should be documented and reported to the health care provider.
Table 9.3a outlines questions used to assess symptoms related to the cardiovascular and peripheral vascular systems. Table 9.3b outlines questions used to assess medical history, medications, and risk factors related to the cardiovascular system. Information obtained from the interview process is used to tailor future patient education by the nurse. [6] , [7] , [8]
Table 9.3a Interview Questions for Cardiovascular and Peripheral Vascular Systems [9]
Follow-Up
Do you ever feel short of breath while sleeping?
How long does it take you to recover?
Have you ever woken up from sleeping feeling suddenly short of breath
(paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)?
Have you noticed your rings, shoes, or clothing feel tight at the end of the day?
Have you noticed any unexplained, sudden weight gain?
Is there anything that makes the swelling better (e.g., sitting with your feet elevated)?
When did palpitations start?
Do you ever feel dizzy?
Did you have any warning signs?
How much activity is needed to cause this pain?
Table 9.3b Interview Questions Exploring Cardiovascular Medical History, Medications, and Cardiac Risk Factors
Have you had any procedures done to improve your heart function, such as ablation or stent placement?
Do you smoke or vape?
If you do not currently smoke, have you smoked in the past?
Are you physically active during the week?
What does a typical day look like in your diet?
Do you drink alcoholic drinks?
Would you say you experience stress in your life?
How many hours of sleep do you normally get each day?
The physical examination of the cardiovascular system involves the interpretation of vital signs, inspection, palpation, and auscultation of heart sounds as the nurse evaluates for sufficient perfusion and cardiac output.
For more information about assessing a patient’s oxygenation status as it relates to their cardiac output, visit the “Oxygenation” chapter in Open RN Nursing Fundamentals.
Equipment needed for a cardiovascular assessment includes a stethoscope, penlight, centimeter ruler or tape measure, and sphygmomanometer. [10]
Interpret the blood pressure and pulse readings to verify the patient is stable before proceeding with the physical exam. Assess the level of consciousness; the patient should be alert and cooperative.
![]()
As a general rule of thumb, findings of systolic blood pressure in adults less than 100,or a pulse rate less than 60 or greater than 100,require immediate follow-up. For more information on obtaining and interpreting vital signs, see the “General Survey” chapter. Keep in mind that excessive drowsiness, restlessness, or irritability can be symptoms of hypoxia.
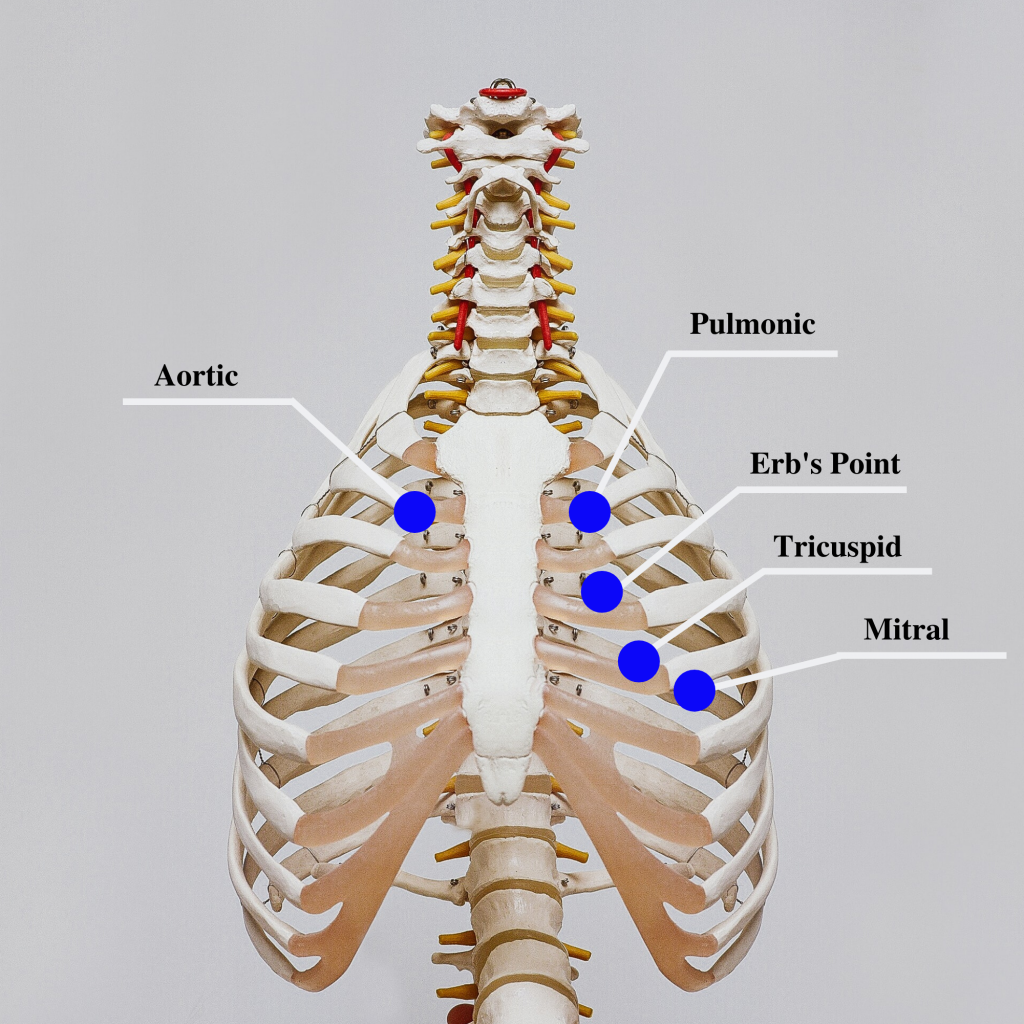
Auscultation is routinely performed over five specific areas of the heart to listen for corresponding valvular sounds. These auscultation sites are often referred to by the mnemonic “APE To Man,” referring to Aortic, Pulmonic, Erb’s point, Tricuspid, and Mitral areas (see Figure 9.8 [17] for an illustration of cardiac auscultation areas). The aortic area is the second intercostal space to the right of the sternum. The pulmonary area is the second intercostal space to the left of the sternum. Erb’s point is directly below the aortic area and located at the third intercostal space to the left of the sternum. The tricuspid (or parasternal) area is at the fourth intercostal space to the left of the sternum. The mitral (also called apical or left ventricular area) is the fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line.
Auscultation usually begins at the aortic area (upper right sternal edge). Use the diaphragm of the stethoscope to carefully identify the S1 and S2 sounds. They will make a “lub-dub” sound. Note that when listening over the area of the aortic and pulmonic valves, the “dub” (S2) will sound louder than the “lub” (S2). Move the stethoscope sequentially to the pulmonic area (upper left sternal edge), Erb’s point (left third intercostal space at the sternal border), and tricuspid area (fourth intercostal space. When assessing the mitral area for female patients, it is often helpful to ask them to lift up their breast tissue so the stethoscope can be placed directly on the chest wall. Repeat this process with the bell of the stethoscope. The apical pulse should be counted over a 60-second period. For an adult, the heart rate should be between 60 and 100 with a regular rhythm to be considered within normal range. The apical pulse is an important assessment to obtain before the administration of many cardiac medications.
The first heart sound (S1) identifies the onset of systole, when the atrioventricular (AV) valves (mitral and tricuspid) close and the ventricles contract and eject the blood out of the heart. The second heart sound (S2) identifies the end of systole and the onset of diastole when the semilunar valves close, the AV valves open, and the ventricles fill with blood. When auscultating, it is important to identify the S1 (“lub”) and S2 (“dub”) sounds, evaluate the rate and rhythm of the heart, and listen for any extra heart sounds.
Listen to a normal S1/S2 sound. It may be helpful to use earbuds or a headphone:![]()
Auscultating Heart Sounds
Extra heart sounds include clicks, murmurs, S3 and S4 sounds, and pleural friction rubs. These extra sounds can be difficult for a novice to distinguish, so if you notice any new or different sounds, consult an advanced practitioner or notify the provider. A midsystolic click, associated with mitral valve prolapse, may be heard with the diaphragm at the apex or left lower sternal border.
A click may be followed by a murmur. A murmur is a blowing or whooshing sound that signifies turbulent blood flow often caused by a valvular defect. New murmurs not previously recorded should be immediately communicated to the health care provider. In the aortic area, listen for possible murmurs of aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation with the diaphragm of the stethoscope. In the pulmonic area, listen for potential murmurs of pulmonic stenosis and pulmonary and aortic regurgitation. In the tricuspid area, at the fourth and fifth intercostal spaces along the left sternal border, listen for the potential murmurs of tricuspid regurgitation, tricuspid stenosis, or ventricular septal defect.
Listen to a heart murmur caused by mitral valve regurgitation:S3 and S4 sounds, if present, are often heard best by asking the patient to lie on their left side and listening over the apex with the bell of the stethoscope. An S3 sound, also called a ventricular gallop, occurs with fluid overload or heart failure when the ventricles are filling. It occurs after the S2 and sounds like “lub-dub-dah,” or a sound similar to a horse galloping. The S4 sound, also called atrial gallop, occurs immediately before the S1 and sounds like “ta-lub-dub.” An S4 sound can occur with decreased ventricular compliance or coronary artery disease. [18]
Listen to a S3 ventricular gallop: Listen to a S4 atrial gallop:A pleural friction rub is caused by inflammation of the pericardium and sounds like sandpaper being rubbed together. It is best heard at the apex or left lower sternal border with the diaphragm as the patient sits up, leans forward, and holds their breath.
The carotid artery may be auscultated for bruits. Bruits are a swishing sound due to turbulence in the blood vessel and may be heard due to atherosclerotic changes.
Palpation is used to evaluate peripheral pulses, capillary refill, and for the presence of edema. When palpating these areas, also pay attention to the temperature and moisture of the skin.
Compare the rate, rhythm, and quality of arterial pulses bilaterally, including the carotid, radial, brachial, posterior tibialis, and dorsalis pedis pulses. Review additional information about obtaining pulses in the “General Survey” chapter. Bilateral comparison for all pulses (except the carotid) is important for determining subtle variations in pulse strength. Carotid pulses should be palpated on one side at a time to avoid decreasing perfusion of the brain. The posterior tibial artery is located just behind the medial malleolus. It can be palpated by scooping the patient’s heel in your hand and wrapping your fingers around so that the tips come to rest on the appropriate area just below the medial malleolus. The dorsalis pedis artery is located just lateral to the extensor tendon of the big toe and can be identified by asking the patient to flex their toe while you provide resistance to this movement. Gently place the tips of your second, third, and fourth fingers adjacent to the tendon, and try to feel the pulse.
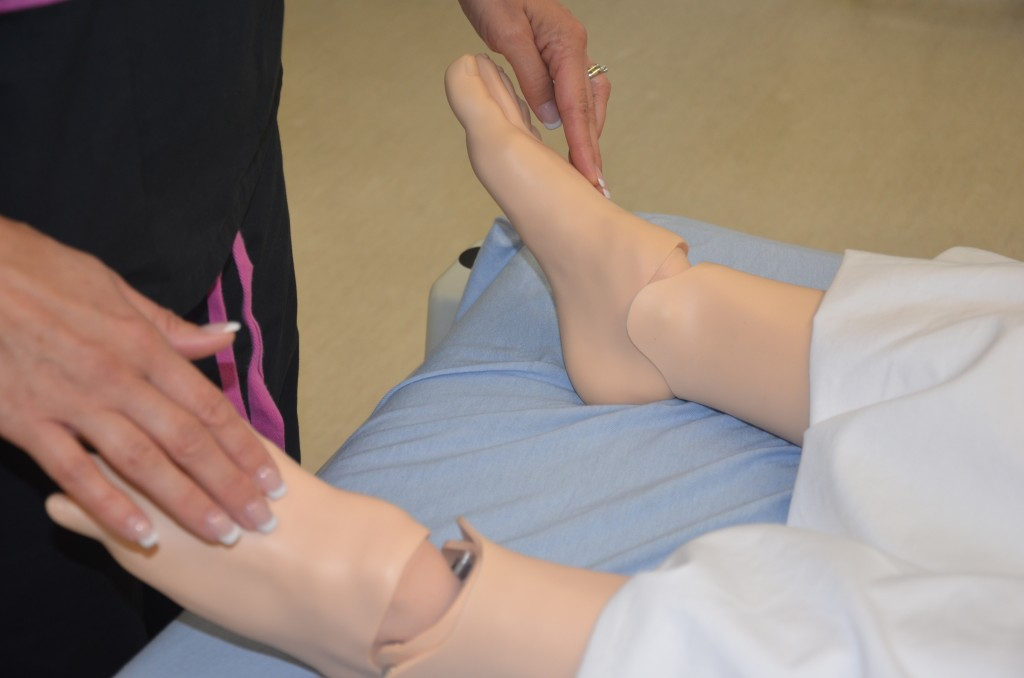
The quality of the pulse is graded on a scale of 0 to 3, with 0 being absent pulses, 1 being decreased pulses, 2 is within normal range, and 3 being increased (also referred to as “bounding”). If unable to palpate a pulse, additional assessment is needed. First, determine if this is a new or chronic finding. Second, if available, use a doppler ultrasound to determine the presence or absence of the pulse. Many agencies use doppler ultrasound to document if a nonpalpable pulse is present. If the pulse is not found, this could be a sign of an emergent condition requiring immediate follow-up and provider notification. See Figures 9.9 [19] and 9.10 [20] for images of assessing pedal pulses.
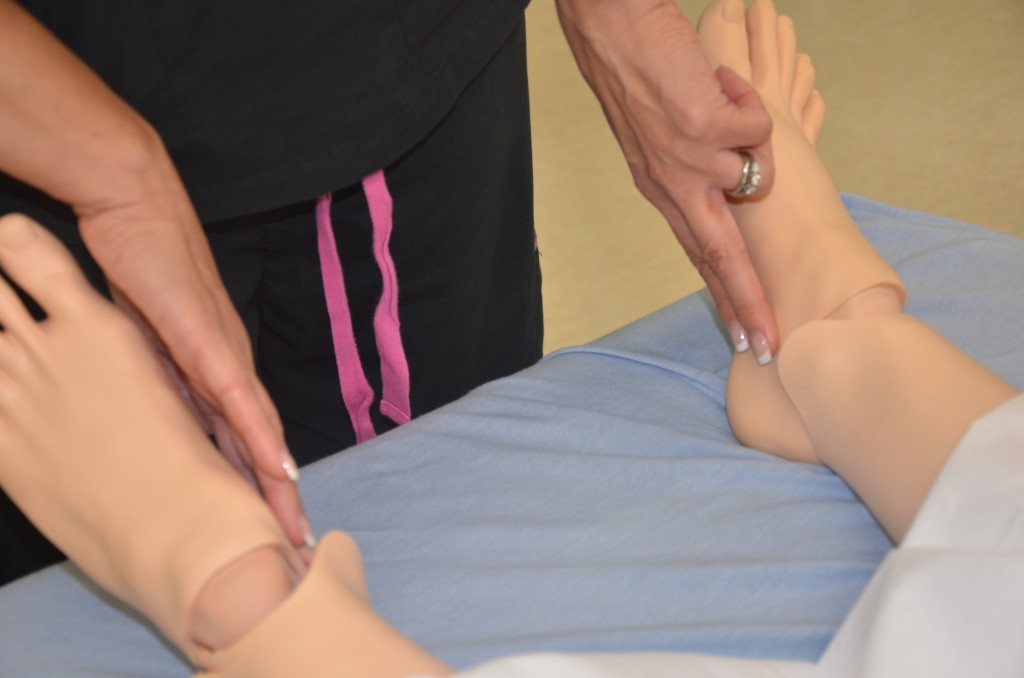 Pulses on simulated patient" width="574" height="380" />
Pulses on simulated patient" width="574" height="380" />
The capillary refill test is performed on the nail beds to monitor perfusion, the amount of blood flow to tissue. Pressure is applied to a fingernail or toenail until it pales, indicating that the blood has been forced from the tissue under the nail. This paleness is called blanching. Once the tissue has blanched, pressure is removed. Capillary refill time is defined as the time it takes for the color to return after pressure is removed. If there is sufficient blood flow to the area, a pink color should return within 2 to 3 seconds after the pressure is removed. [21]
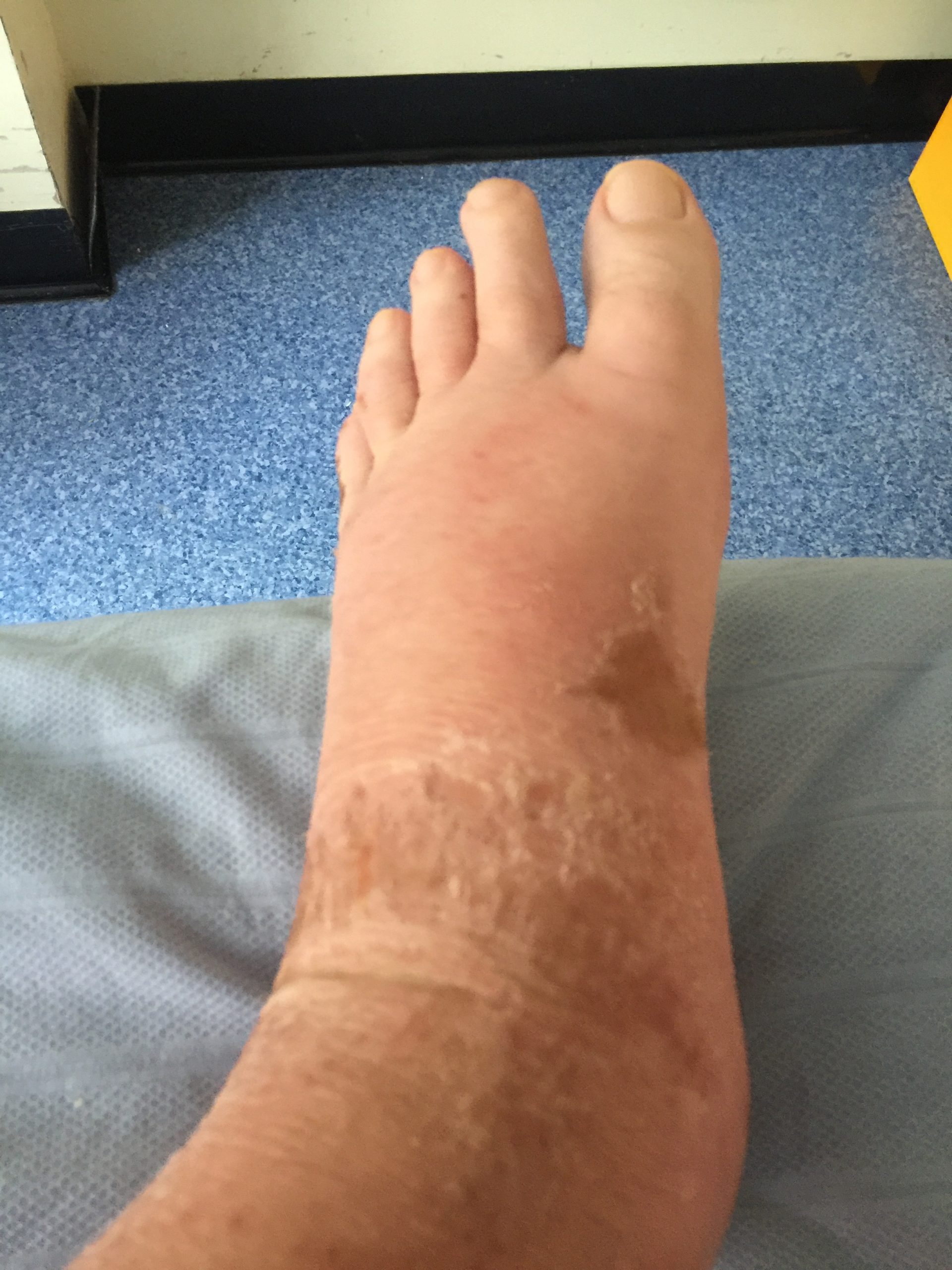
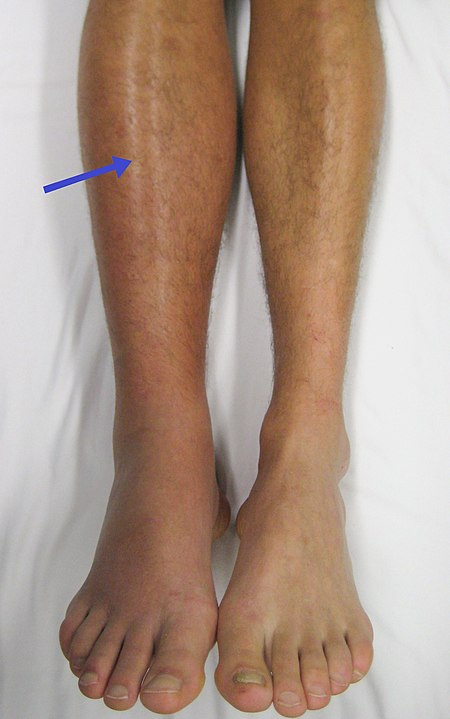
Edema occurs when one can visualize visible swelling caused by a buildup of fluid within the tissues. If edema is present on inspection, palpate the area to determine if the edema is pitting or nonpitting. Press on the skin to assess for indentation, ideally over a bony structure, such as the tibia. If no indentation occurs, it is referred to as nonpitting edema. If indentation occurs, it is referred to as pitting edema. See Figure 9.11 [22] for images demonstrating pitting edema.
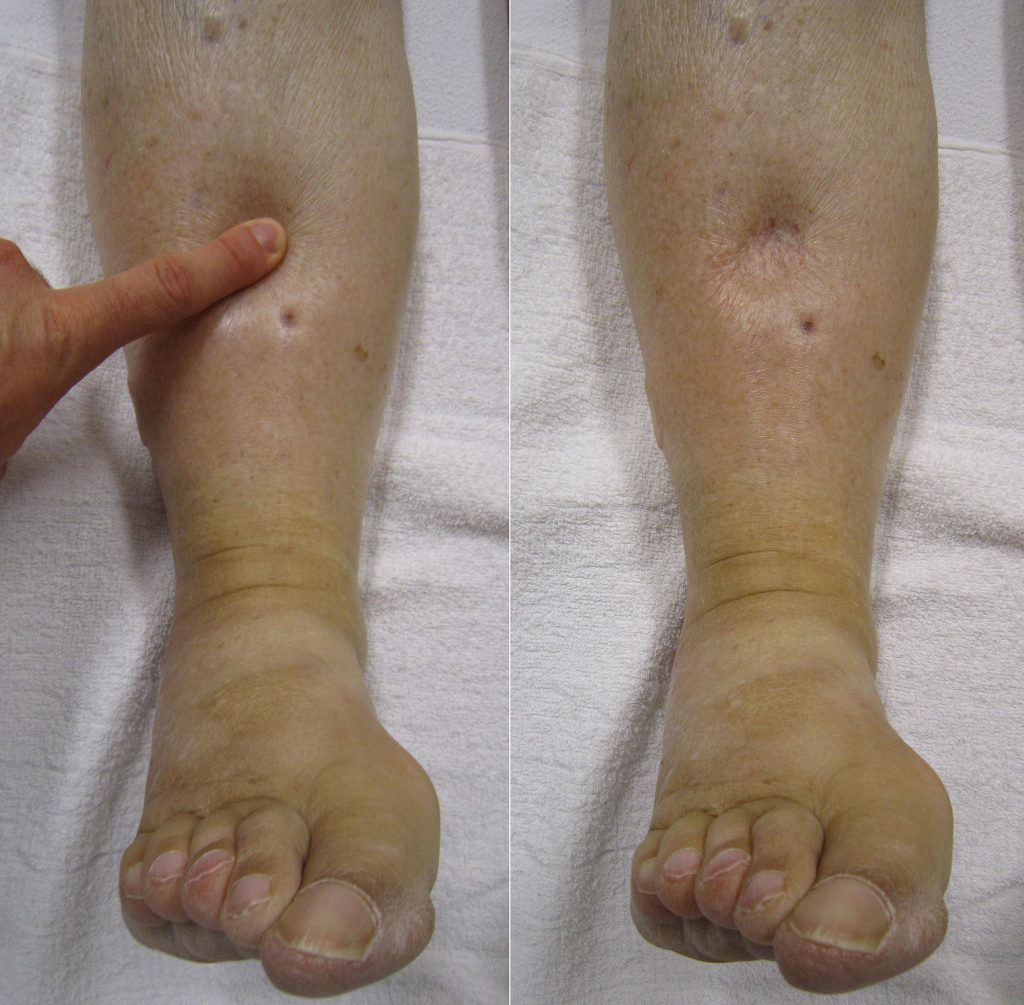
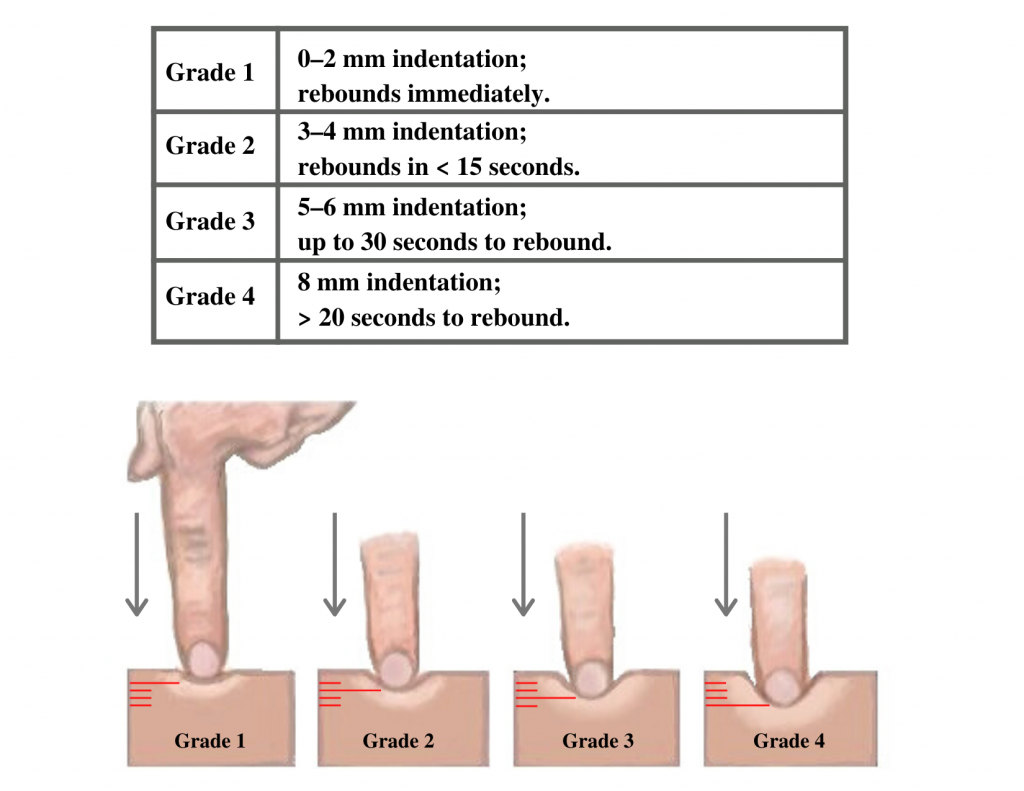
Note the depth of the indention and how long it takes for the skin to rebound back to its original position. The indentation and time required to rebound to the original position are graded on a scale from 1 to 4. Edema rated at 1+ indicates a barely detectable depression with immediate rebound, and 4+ indicates a deep depression with a time lapse of over 20 seconds required to rebound. See Figure 9.12 [23] for an illustration of grading edema. Additionally, it is helpful to note edema may be difficult to observe in larger patients. It is also important to monitor for sudden changes in weight, which is considered a probable sign of fluid volume overload.
You may observe advanced practice nurses and other health care providers palpating the anterior chest wall to detect any abnormal pulsations the underlying cardiac chambers and great vessels may produce. Precordial movements should be evaluated at the apex (mitral area). It is best to examine the precordium with the patient supine because if the patient is turned on the left side, the apical region of the heart is displaced against the lateral chest wall, distorting the chest movements. [24] A heave or lift is a palpable lifting sensation under the sternum and anterior chest wall to the left of the sternum that suggests severe right ventricular hypertrophy. A thrill is a vibration felt on the skin of the precordium or over an area of turbulence, such as an arteriovenous fistula or graft.
The cardiovascular assessment and expected findings should be modified according to common variations across the life span.
A murmur may be heard in a newborn in the first few days of life until the ductus arteriosus closes.
When assessing the cardiovascular system in children, it is important to assess the apical pulse. Parameters for expected findings vary according to age group. After a child reaches adolescence, a radial pulse may be assessed. Table 9.3c outlines the expected apical pulse rate by age.
Table 9.3c Expected Apical Pulse by Age
| Age Group | Heart Rate |
|---|---|
| Preterm | 120-180 |
| Newborn (0 to 1 month) | 100-160 |
| Infant (1 to 12 months) | 80-140 |
| Toddler (1 to 3 years) | 80-130 |
| Preschool (3 to 5 years) | 80-110 |
| School Age (6 to 12 years) | 70-100 |
| Adolescents (13 to 18 years) | 60-90 |
In adults over age 65, irregular heart rhythms and extra sounds are more likely. An “irregularly irregular” rhythm suggests atrial fibrillation, and further investigation is required if this is a new finding. See the hyperlink in the box below for more information about atrial fibrillation.
Listen to atrial fibrillation: For more information on atrial fibrillation, visit the following web page: CDC Atrial Fibrillation.After completing a cardiovascular assessment, it is important for the nurse to use critical thinking to determine if any findings require follow-up. Depending on the urgency of the findings, follow-up can range from calling the health care provider to calling the rapid response team. Table 9.3d compares examples of expected findings, meaning those considered within normal limits, to unexpected findings, which require follow-up. Critical conditions are those that should be reported immediately and may require notification of a rapid response team.
Table 9.3d Expected Versus Unexpected Findings on Cardiac Assessment
| Assessment | Expected Findings | Unexpected Findings (Document and notify the provider if this is a new finding*) |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Apical impulse may or may not be visible | Scars not previously documented that could indicate prior cardiac surgeries |
Heave or lift observed in the precordium
Symptomatic bradycardia (HR
New systolic blood pressure (
Orthostatic blood pressure changes (see “Blood Pressure” chapter for more information)
New irregular heart rhythm
New extra heart sounds such as a murmur, S3, or S4
New abnormal cardiac rhythm changes
See Table 9.3e for a comparison of expected versus unexpected findings when assessing the peripheral vascular system.
Table 9.3e Expected Versus Unexpected Peripheral Vascular Assessment Findings
Equal hair distribution on upper and lower extremities
Absence of jugular vein distention (JVD)
Absence of edema
Decreased or unequal hair distribution
Presence of jugular vein distention (JVD) in an upright position or when head of bed is 30-45 degrees
New or worsening edema
Rapid and unexplained weight gain
Pulses present and equal bilaterally
Absence of edema
Absent, weak/thready, or bounding pulses
New irregular pulse
New or worsening edema
Capillary refill greater than 2 seconds
Absent pulse (and not heard using Doppler device)
Capillary refill time greater than 3 seconds